This document is DRAFT. Procedure, settings and images may be changed without notice.
This article describes how to configure a system so that an organization's most sensitive information is only accessible to those users with sufficient security clearance.
Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 can be used to enforce Microsoft Digital Rights Management (DRM; also known as Information Rights Management - IRM) to messages and Office file attachments. Transport Rules in the Exchange Server can be configured to ensure that a DRM Template is applied to messages of a certain security classification, based on its security classification label (protective marking).
Background
Information Security Classification Policy
The organization's Information Security Classification Policy stipulates that all email messages must be classified. The policy allows for the following security classifications:
- UNCLASSIFIED
- CONFIDENTIAL
- SECRET
The organization uses an email classification client, such as Janusseal for Outlook, to force end-users to classify all email messages they send.
Information Security Policy
The organization's Information Security Policy stipulates that
- information should be accessed on a need-to-know basis
- users require relevant security clearance to access classified information
- UNCLASSIFIED and CONFIDENTIAL information can be emailed 'in-the-clear' (without any encryption)
- SECRET information should be only ever be emailed in an encrypted form using Microsoft DRM.
System Description
The system consists of the following components:
- A Windows 2008 Active Directory
- A Windows Server 2008 R2 Active Directory Rights Management Server
- A Microsoft Exchange 2010 SP1 or SP2 Server in Hub Transport Role
- Windows workstations (either Windows XP SP3, Windows Vista SP1 or Windows 7), which are members of the Windows domain with
- Microsoft Office (2003 or later)
- Janusseal for Outlook, Janusseal for OWA, or some other email classification client add-on
- Microsoft Rights Management client
System Design
Active Directory Groups
Active Directory Security Groups are used to define which each users security clearance.
- All Domain Users will have CONFIDENTIAL clearance.
- A security group, "SECRET Users", will include all those users with SECRET security clearance.
Active Directory Rights Management Server
Active Directory Rights Management Server (RMS) will be used to define a single Rights Policy Template (named SECRET Access), which will be used to provide full access to information for users with SECRET clearance. Users without SECRET clearance will not have any access to the information.
Exchange 2010 Server
A Transport Rule in Exchange 2010 Server will be used to detect email messages which:
- have been sent by a staff member (so internal in origin)
- contain a security classification label (protective marking) that indicate the message is SECRET
For such messages, the Transport Rule will apply a DRM Template that is used for SECRET information to the message contents, including any Office file attachments.
System Implementation
TODO: Introduction
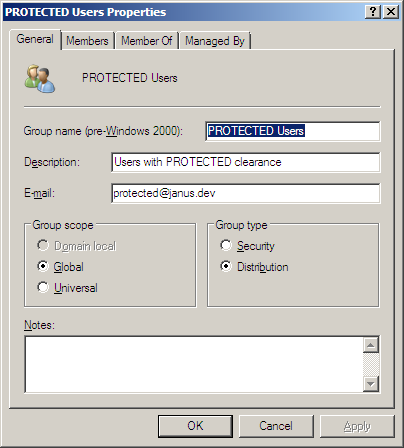
Active Directory Security Group: SECRET Users
Build a new Active Directory Security Group, named SECRET Users. The group needs an email address, which is used to link the Group with the SECRET Distributed Rights Policy Template.
Add users to this group who have SECRET security clearance.
TODO: Change the screenshot to show the Group type as a Security group; change name of group from PROTECTED Users to SECRET Users
Active Directory Rights Management Server
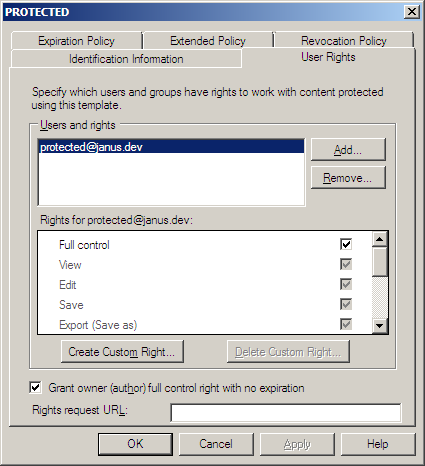
TODO: procedure to create SECRET Access DRM template.
TODO: update the screenshot to show the title as SECRET Access
Exchange 2010 Server
The proceduce described below is an enhancement of that described by Microsoft at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd302432.aspx; the procedure here describes the select conditions which are used to identify SECRET classified messages sent from internal senders.
- On the Exchange 2010 Server in Hub Transport Role, start the Exchange Management Console
- In the Exchange Management Console, navigate to Organization Configuration > Hub Transport.
- In the action pane, click New Transport Rule.
- On the Introduction page of the wizard, complete the following fields:
Name = DRM encrypt SECRET messages
Comments (optional) You can use this field to describe the rule's functionality, and relevant details such as a change request or trouble ticket number, date, and name of the administrator. Text in this field has no impact on rule functionality.
Enabled New rules are enabled by default. If you want the rule to be created in a disabled state, clear the check box. - On the Conditions page of the wizard, complete the following fields:
- In the Step 1. Select Condition(s) box, select the conditions
- from users that are inside or outside the organization - set to inside
- when the Subject field contains specific words - set to detect [SEC=SECRET
- In the Step 1. Select Condition(s) box, select the conditions
- On the Actions page of the wizard, complete the following fields:
- In the Step 1. Select actions box, select rights protect message with RMS template.
- In the Step 2: Edit the rule description by clicking an underlined value box, click the underlined words RMS template.
- In the Select RMS template dialog box, select the SECRET Access RMS template, and then click OK.
- (Optional) On the Exceptions page of the wizard, select an exception you want to use, and then type the appropriate value if required.
- On the Create Rule page of the wizard, review the Configuration Summary to make sure the predicates and values used in the conditions and any exceptions appear as expected. Make sure the RMS template selected is SECRET Access.
- Click New to create the transport rule.
- On the Completion page, review the following, and then click Finish to close the wizard:
A status of Completed indicates that the wizard completed the task successfully.
A status of Failed indicates that the task wasn't completed. If the task fails, review the summary for an explanation, and then click Back to make any configuration changes.
Check List / Troubleshooting
TODO: Check the Windows DRM Client is operating on the workstation.
TODO: Check the user and that MS Office has access to the policies.
Log onto a workstation as a user without SECRET clearance.
Check the following:
- Microsoft Office is operating (Start MS Word)
If failed:
- Install Microsoft Office on the workstation
Log onto a workstation as a user with SECRET clearance.
Check the following:
- Microsoft Office is operating (Start MS Word)
- Create a new Word document, apply the SECRET Access DRM plolicy to the Word document
If failed:
System Testing
TBD
An UNCLASSIFIED email...
... sent with no DRM template applied
A SECRET email...
received with SECRET Access DRM applied:
Security Precautions
The following threats should be managed by the organization to maximise compliance. Note that this list is not exhaustive, and organisations must carry out there own threat and risk assessment for their own circumstances. This list is provided only as a starting point.
- Users who can modify the Actice Directory User Groups or the Distributed Rights Policy Templates will be able to change who can access SECRET messages.
- If the template policy file is inaccessible to the Office application, the DRM
policy template will not be applied. This could occur if the policy files have not been published to the workstations, or if the registry keys which are used by Office to locate the policy files have been modified. - If the template policy file is corrupted (eg the digital signature cannot be verified) or inaccessible to the Office application, the DRM policy template will not be applied.

